❌ How You Should Not Architect an Application
When it comes to building software, most people focus on <em>best practices</em> and the right patterns to follow. But knowing what <strong>not</strong> to do is equally important. A poorly designed architecture can lead to slow development, frustrated engineers, expensive fixes, and in the worst cases, complete project failure.
In this article, we'll go over some of the most common mistakes and <em>anti-patterns</em> that developers and architects should avoid when designing modern applications.
🚫 1. Skipping Clear Requirements
One of the biggest mistakes is jumping straight into coding without fully understanding the problem you're solving. This often leads to <strong>scope creep</strong>, unnecessary complexity, and solutions that don't meet user needs.
<em>Bad Example:</em> Building a complex recommendation engine when all you really needed was a simple search filter.
🚫 2. The Monolithic Ball of Mud
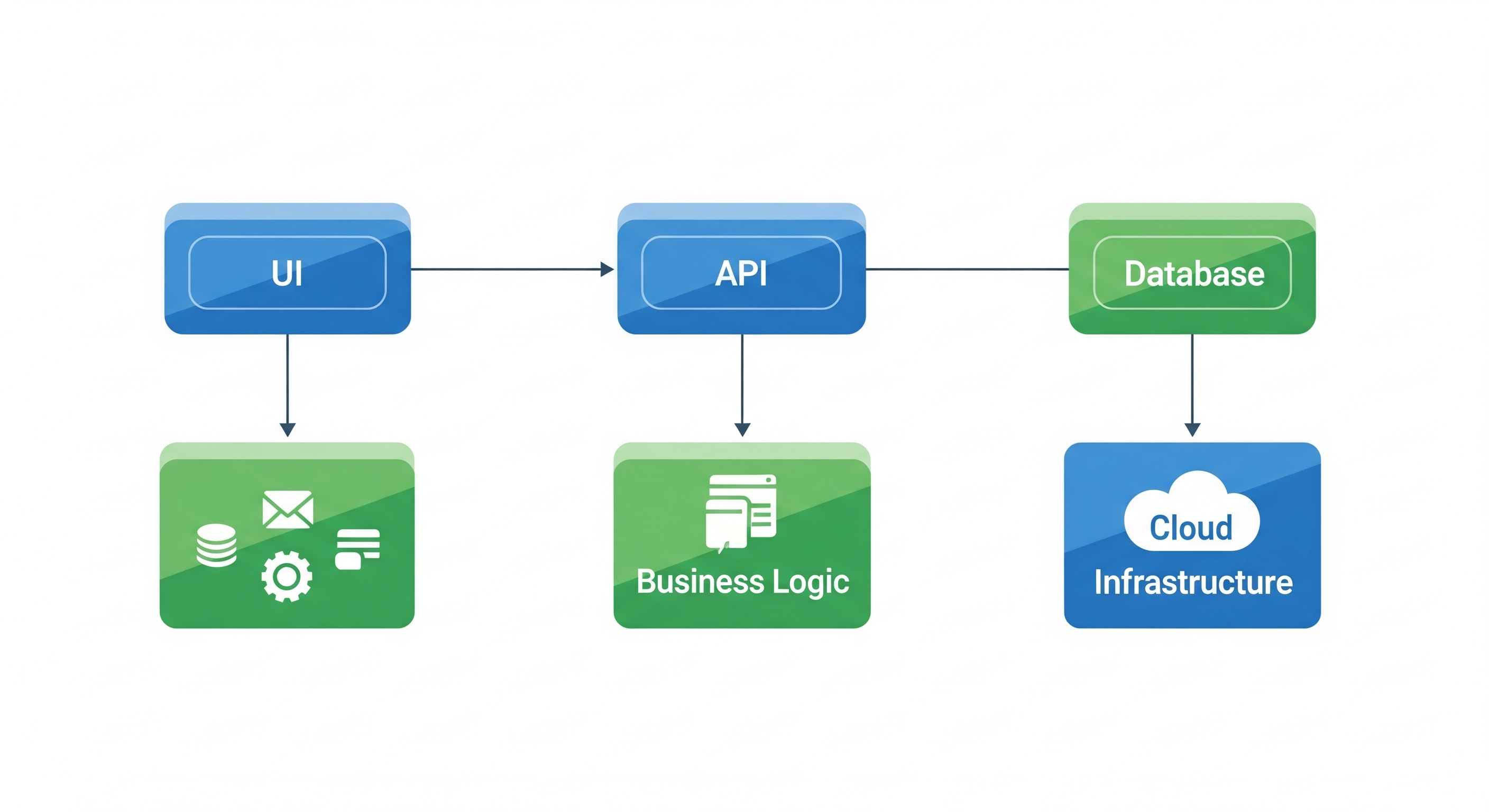
A monolithic application is not always bad, but the problem arises when everything is <strong>tightly coupled</strong> with no modularity. Business logic, database queries, and presentation code end up tangled together, making the system fragile and hard to scale.
<em>Why it's bad:</em> Adding a new feature may break five unrelated ones. Scaling one part of the system requires scaling the entire application.
🚫 3. Premature Microservices
Microservices are popular, but they are <strong>not</strong> a silver bullet. Splitting an early-stage app into dozens of services creates unnecessary complexity with deployments, monitoring, and communication overhead.
<em>Rule of Thumb:</em> Start with a simple, modular monolith. Extract microservices only when you have clear bottlenecks.
🚫 4. Ignoring Scalability & Fault Tolerance
Designing only for the happy path is a recipe for disaster. Real-world systems fail. Databases go down, APIs time out, and networks get flaky.
- ❌ No retry logic or circuit breakers → your app collapses with one failure.
- ❌ Single-threaded APIs for high traffic apps → instant bottlenecks.
- ❌ No caching strategy → unnecessary load on the database.
🚫 5. Tight Coupling Everywhere
When layers of your system depend too heavily on each other, changing one piece forces changes everywhere. For example, if your UI directly queries the database, swapping databases becomes impossible without rewriting your frontend.
Instead, follow <strong>separation of concerns</strong> and use clear interfaces between components.
🚫 6. Ignoring Security from Day One
Security is often treated as an afterthought, but it should be a foundation. Some common mistakes include:
- ❌ Hardcoding API keys and secrets in code.
- ❌ Using weak authentication and skipping authorization checks.
- ❌ Not encrypting sensitive data like passwords and tokens.
Security debt is harder to fix than technical debt — attackers don't wait for you to patch things up.
🚫 7. Overengineering
It's tempting to use the latest buzzwords and complex patterns, but adding unnecessary layers of complexity slows you down. Don't bring in Kafka, Kubernetes, CQRS, and event sourcing just because they sound cool — especially for a simple blog or CRUD app.
<em>Golden rule:</em> Build only what you need today, but design so you can extend tomorrow.
🚫 8. Lack of Observability
Running an app in production without logging, monitoring, or alerting is like flying a plane with no instruments. When things break — and they will — you'll be blind.
Make sure you have:
- ✅ Structured logs for debugging.
- ✅ Metrics to understand performance.
- ✅ Alerts to notify you before users complain.
- ✅ Traces to follow requests across services.
🚫 9. No Documentation or Standards
Every developer coding in their own style with no documentation or architectural diagrams leads to confusion and wasted time. Tribal knowledge makes it impossible for new engineers to onboard quickly.
Maintain coding guidelines, architectural decision records (ADRs), and simple diagrams to keep everyone aligned.
🚫 10. Single Points of Failure
If one server, one database, or even one component failing can take down your whole system, you have a serious design flaw. Redundancy and backups are non-negotiable in production systems.
🧩 Why Avoiding These Mistakes Matters
Every shortcut in architecture becomes a bottleneck later. What starts as small inefficiencies eventually snowballs into massive technical debt. Teams spend more time fighting fires than delivering features.
🌟 Final Thoughts
Good architecture is not about making things more complex — it's about making the right trade-offs. Avoiding these common anti-patterns will save your team time, money, and countless headaches.
"Great systems are not the ones with the most patterns, but the ones with the fewest mistakes."